使用nginx部署多个前端项目的几种方式
基于域名配置
基于端口配置
基于location配置
在正式开始之前,我们先来看一下nginx安装的默认配置文件: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 文件
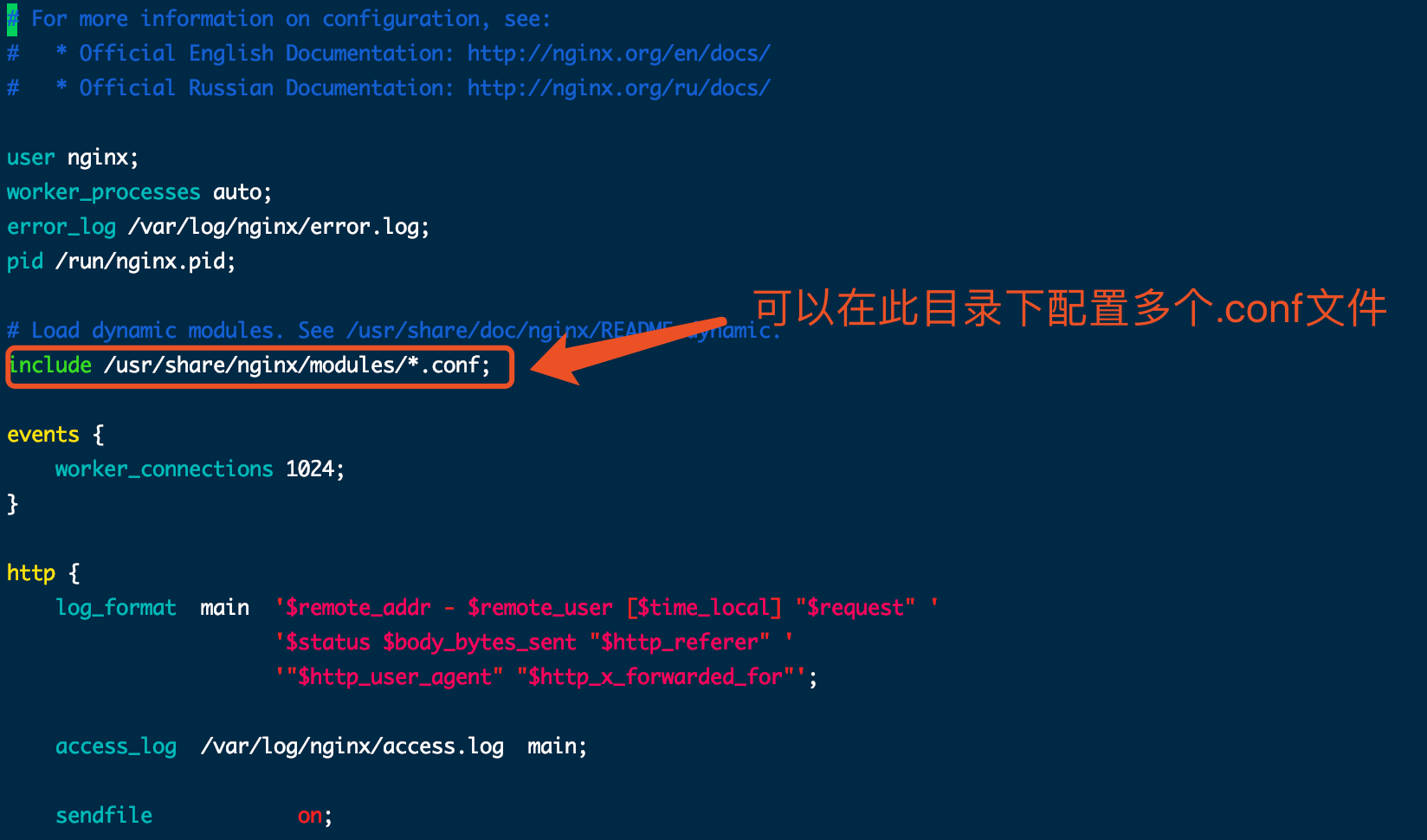
可以看到图中的:include /usr/nginx/modules/*.conf,这句话的作用就是可以在nginx启动加载所有 /usr/nginx/modules/ 目录下的 *.conf 文件。 所以,平时我们为了方便管理,可以在此目录下面定义自己的 xx.conf 文件即可。
基于域名配置
基于域名配置,前提是先配置好了域名解析。比如说你自己买了一个域名:www.fly.com。 然后你在后台配置了2个它的二级域名: a.fly.com、 b.fly.com。
配置文件如下:
配置 a.fly.com 的配置文件:
vim /usr/nginx/modules/a.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name a.fly.com;
location / {
root /data/web-a/dist;
index index.html;
}
}
配置 b.fly.com 的配置文件:
vim /usr/nginx/modules/b.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name b.fly.com;
location / {
root /data/web-b/dist;
index index.html;
}
}
这种方式的好处是主机只要开放80端口即可。然后访问的话直接访问二级域名就可以访问。
基于端口配置
配置文件如下:
配置 a.fly.com 的配置文件:
vim /usr/nginx/modules/a.conf
server {
listen 8000;
location / {
root /data/web-a/dist;
index index.html;
}
}
# nginx 80端口配置 (监听a二级域名)
server {
listen 80;
server_name a.fly.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000; #转发
}
}
配置 b.fly.com 的配置文件:
vim /usr/nginx/modules/b.conf
server {
listen 8001;
location / {
root /data/web-b/dist;
index index.html;
}
}
# nginx 80端口配置 (监听b二级域名)
server {
listen 80;
server_name b.fly.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8001; #转发
}
}
可以看到,这种方式一共启动了4个server,而且配置远不如第一种简单,所以不推荐。
基于location配置
配置文件如下:
配置 a.fly.com 的配置文件:
vim /usr/nginx/modules/ab.conf
server {
listen 80;
location / {
root /data/web-a/dist;
index index.html;
}
location /web-b {
alias /data/web-b/dist;
index index.html;
}
}
注意: 这种方式配置的话,location / 目录是root,其他的要使用alias。
可以看到,这种方式的好处就是我们只有一个server,而且我们也不需要配置二级域名,并且前端项目里要配置二级目录。
nginx location 目录匹配详解
nginx location 加不加 / 匹配原则
nginx每个location都是一个匹配目录,nginx的策略是:访问请求来时,会对访问地址进行解析,从上到下逐个匹配,匹配上就执行对应location大括号中的策略,并根据策略对请求作出相应。
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost; # http://localhost/wddd01/xxx -> http://localhost:8080/wddd01/xxx
location /wddd01/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
}
# http://localhost/wddd02/xxx -> http://localhost:8080/xxx
location /wddd02/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/;
}
# http://localhost/wddd03/xxx -> http://localhost:8080/wddd03*/xxx
location /wddd03 {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
}
# http://localhost/wddd04/xxx -> http://localhost:8080//xxx,请注意这里的双斜线,好好分析一下。
location /wddd04 {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/;
}
# http://localhost/wddd05/xxx -> http://localhost:8080/hahaxxx,请注意这里的haha和xxx之间没有斜杠,分析一下原因。
location /wddd05/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/haha;
}
# http://localhost/api6/xxx -> http://localhost:8080/haha/xxx
location /wddd06/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/haha/;
}
# http://localhost/wddd07/xxx -> http://localhost:8080/haha/xxx
location /wddd07 {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/haha;
}
# http://localhost/wddd08/xxx -> http://localhost:8080/haha//xxx,请注意这里的双斜杠。
location /wddd08 {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/haha/;
}
}
location目录后加"/",只能匹配目录,不加“/”不仅可以匹配目录还对目录进行模糊匹配。而proxy_pass无论加不加“/”,代理跳转地址都直接拼接。

 微信收款码
微信收款码 支付宝收款码
支付宝收款码